Coverage Distance
What is Coverage Distance?
Coverage distance refers the total area covered by your camera . It can change depending on your camera and set up.
How to Calculate Coverage Distance
Example scenario: The goal is to fly transects at 5-10m range from bottom, at 0.5m/s (1 knot) taking images continuously for 80% overlap. The images will be post-processed into an ortho-mosaic referenced to world position. To achieve this:
Place the LED as far from the camera as possible, which will avoid lighting the water between the camera and the subject. This will limit backscatter and give the subject more contrast and clarity. See section on backscatter.
The camera should be positioned facing straight down if processing for ortho-mosaic.
The LED(s) should be positioned at an angle to overlap the field of view, taking into account the full altitude range that the system will be flying.
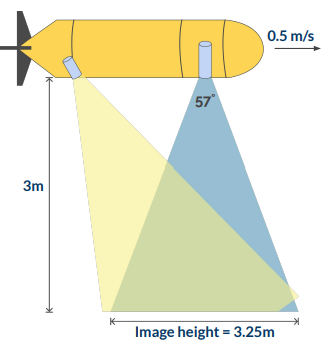
Camera vertical FOV (57°) with distance to seafloor (3m) gives vertical image coverage:
Image height = 2 * distance * tan (vertical FOV / 2)
Image height = 2 * 3m * tan(57/2) = 3.25mBased on the mission velocity (0.5m/s) and necessary overlap (80%), the image period should be set to: Image period = (image height - (image height * overlap %)) / velocity Image period = (3.25m - (3.25m * 0.8)) / 0.5m/s = 1.3sec (set the camera to 2Hz)
Based on how fast the scene will be moving, approximate 1/200 shutter speed should be acceptable.
Adjust LED output setting and test with camera to avoid under or over exposure of the images.
Water attenuates light much more than air, even over short distances.
Therefore, in-air testing of strobe intensity is not sufficient.
